Table of contents
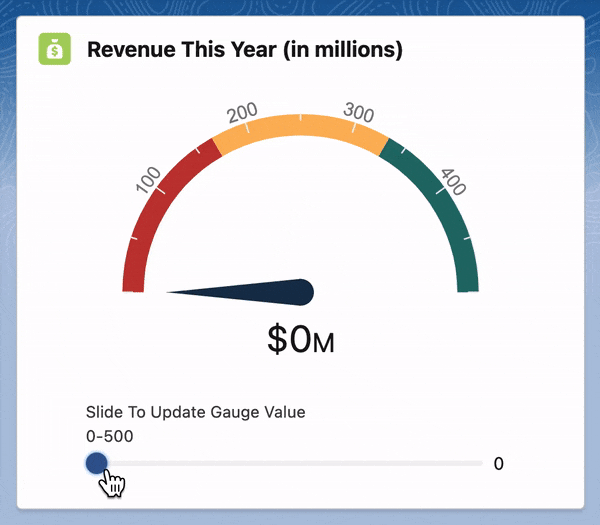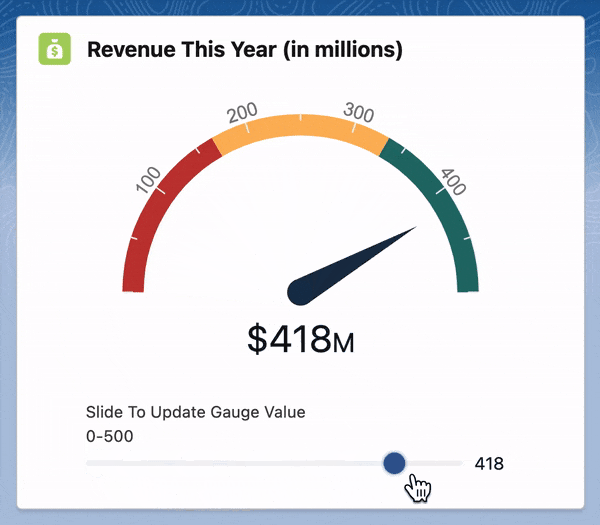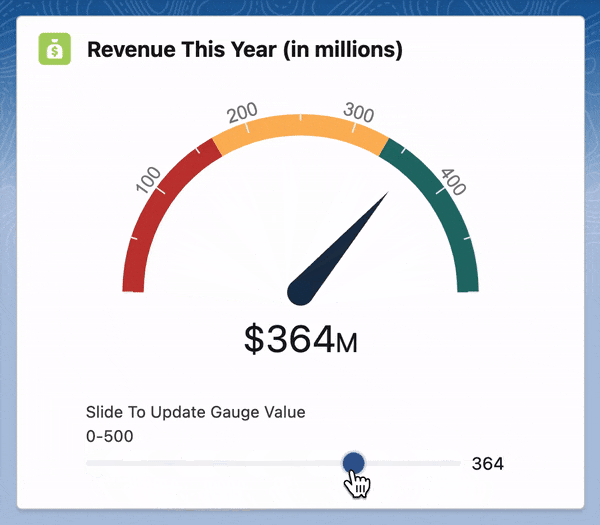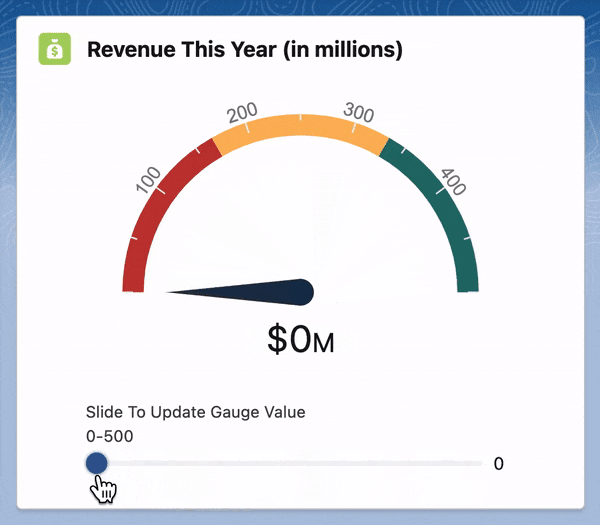
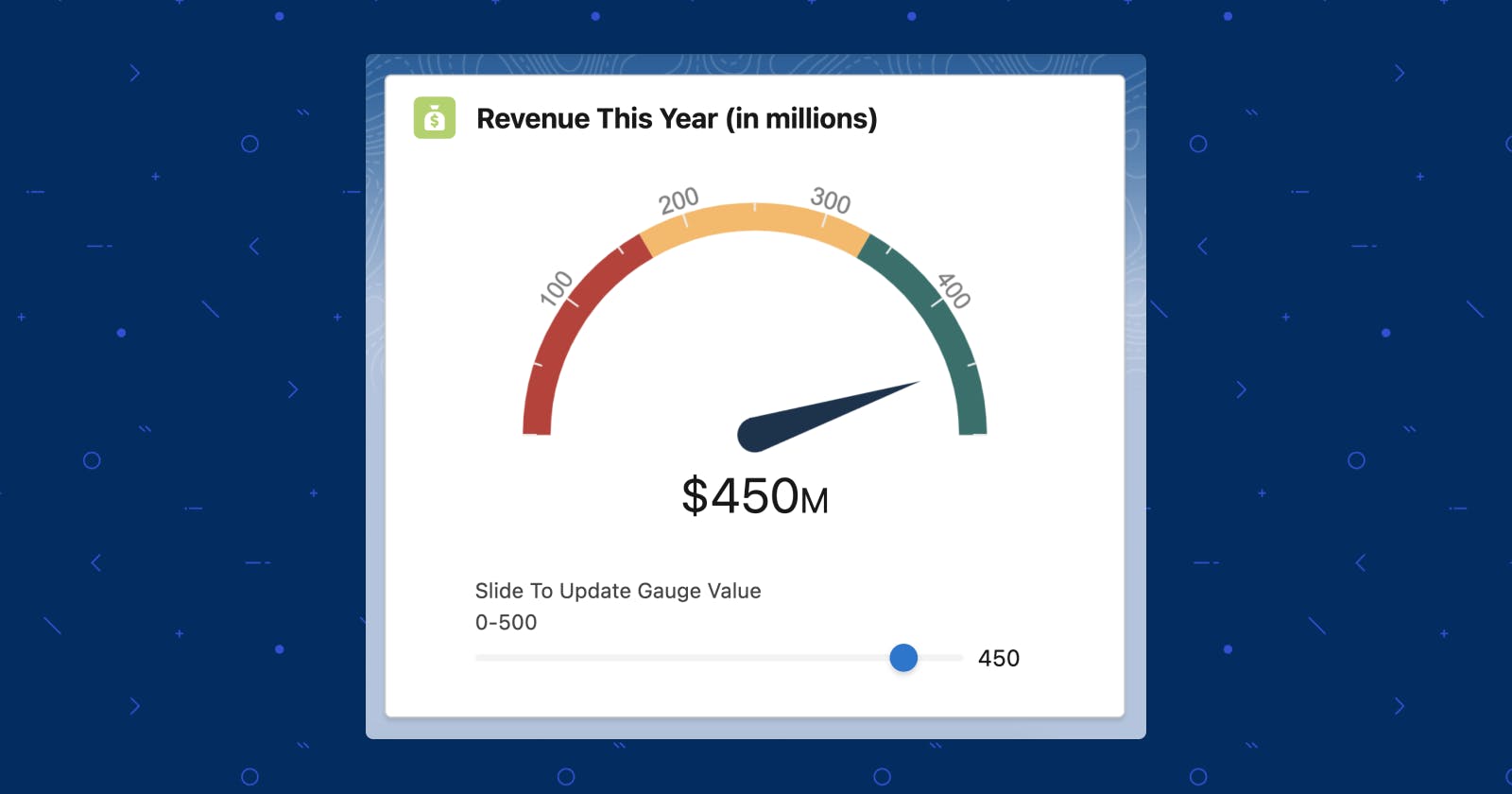
For this, we will be using a JavaScript library called Gauge.js. Let's get started!
📜 Add The Library To Static Resources
Here is how:
Click the button gauge.min.js (second button below the heading on the top of the page)
You should be taken to https://bernii.github.io/gauge.js/dist/gauge.min.js
Save the file onto your machine
Upload to Static Resources with the name
gaugeJS
🔮 Create The Chart
gaugeChart.html
<template>
<lightning-card variant="Narrow" title="Revenue This Year (in millions)" icon-name="custom:custom17">
<div class="slds-card__body slds-card__body_inner">
<!-- Gauge.js uses HTML canvas element to create charts so here is one -->
<center>
<canvas style="width:85%" lwc:ref="chart" lwc:dom="manual"></canvas>
</center>
<!-- Element to show the current Gauge value -->
<div class="slds-text-heading_large slds-text-align_center">
$
<span lwc:ref="gaugeValue" lwc:dom="manual"></span>
<span class="slds-text-heading_medium">M</span>
</div>
<!-- Example slider to demonstrate how to update the gauge value -->
<div class="slds-m-vertical_large slds-grid slds-grid_align-center">
<lightning-slider label="Slide To Update Gauge Value" size="medium" value="450" max="500"
onchange={handleSliderChange}>
</lightning-slider>
</div>
</div>
</lightning-card>
</template>
gaugeChart.js
import { LightningElement, track } from 'lwc';
import { loadScript } from "lightning/platformResourceLoader";
import gaugeJS from '@salesforce/resourceUrl/gaugeJS';
export default class GaugeChart extends LightningElement {
// Think of this like a global variable, it holds the reference to chart we'll be drawing so the chart can be modified from other methods
@track chart;
// Gauge chart config
chartConfig = {
angle: 0, // The span of the gauge arc
lineWidth: 0.12, // The line thickness
radiusScale: 1, // Relative radius
pointer: {
length: 0.40, // // Relative to gauge radius
strokeWidth: 0.06, // The thickness
color: '#17324D' // Fill color
},
staticZones: [ // The red, yellow, green coloured zones on the gauge
{
strokeStyle: '#C23934',
min: 0,
max: 167
},
{
strokeStyle: '#FDB75D',
min: 167,
max: 333
},
{
strokeStyle: '#24716B',
min: 333,
max: 500
}
],
staticLabels: {
font: "14px Arial",
labels: [100, 200, 300, 400], // Print labels at these values
color: "#818181", // Optional: Label text color
fractionDigits: 0 // Optional: Numerical precision. 0=round off.
},
renderTicks: { // The grey tick lines on the gauge
divisions: 5,
divWidth: 0.6,
divLength: 0.5,
divColor: '#ecebea',
subDivisions: 2,
subLength: 0.3,
subWidth: 0.6,
subColor: '#ecebea'
},
limitMin: false, // If true, the min value of the gauge will be fixed
limitMax: false, // If false, max value increases automatically if value > maxValue
colorStart: '#6FADCF', // Colors
colorStop: '#8FC0DA', // just experiment with them
strokeColor: '#E0E0E0', // to see which ones work best for you
generateGradient: true,
highDpiSupport: true // High resolution support
};
connectedCallback() {
// Load Gauge.js
loadScript(this, gaugeJS).then(() => {
// HTML canvas for gauge chart
const gaugeChartElement = this.refs.chart;
// HTML element for animated number counter
const gaugeValueHolder = this.refs.gaugeValue;
if(gaugeChartElement && gaugeValueHolder) {
// Draw the gauge chart
this.chart = new Gauge(gaugeChartElement).setOptions(this.chartConfig);
// You can also set other chart options this way
this.chart.maxValue = 500;
this.chart.setTextField(gaugeValueHolder);
this.chart.setMinValue(0);
this.chart.animationSpeed = 10;
this.chart.set(450);
}
});
}
handleSliderChange(evt) {
// Get the slider value
let newGaugeValue = Number(evt.currentTarget.value)
// Update the gauge with the new slider value
this.chart.set(newGaugeValue);
}
}
this.chart.set(<number>) is the method that is used to update the Gauge chart value after the chart is drawn.
Happy Charting! 🚀